Cardiology

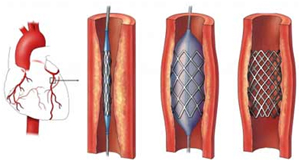 |
India Surgery Coronary Stenting Surgery, India Cost Coronary Stening, Coronary Stenting Surgery, India Coronary Stening, India Low Cost Coronary Stenting, India Stent, India Cardiovascular Disease, India Heart Medicine, India Alternative Medicine, India Coronary Angioplasty, India Angioplasty,India Medical Treatment,India Drug Eluting Coronary Stenting Surgery, India Cost Coronary Stenting Surgery, India Surgery Tour, India Hospitals,India Coronary Artery Bypass, India CABG, India Open Heart Surgery